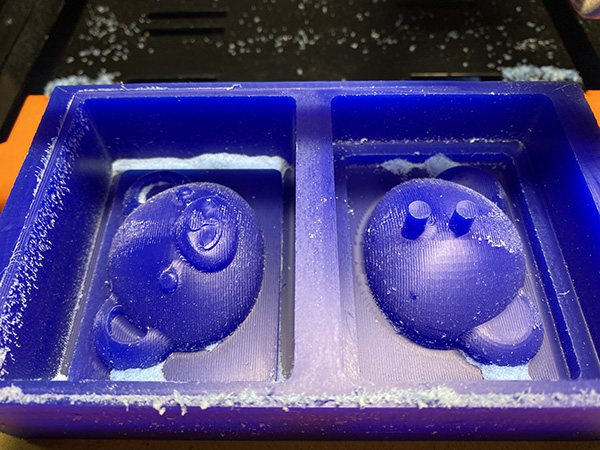
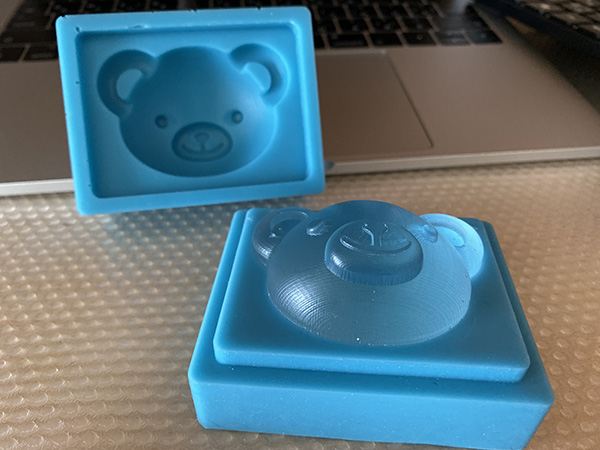
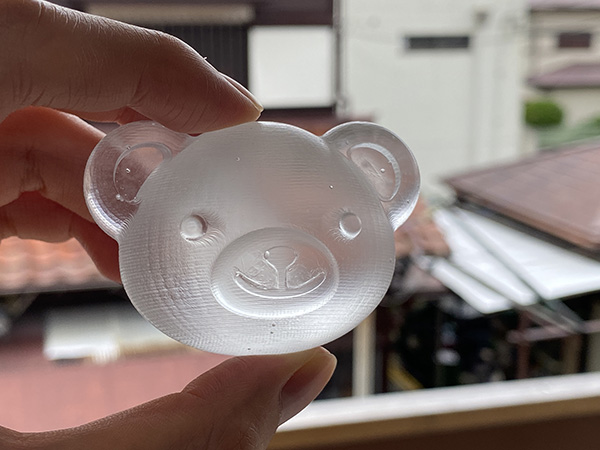
Week 12. Molding and Casting#
- Authors :
Jun Kawahara,Kai Naito,Asako Okazaki,Georg Tremmel,Kae Nagano - Created :
3/1/2019, Last Update:4/20/2025
Assignments#
Individual Assignments#
- Design a mold around the process you’ll be using, produce it with a smooth surface finish that does not show the production process, and use it to cast parts.
Group assignment#
- Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials
- Make and compare test casts with each of them
- Compare mold making processes ( printing vs milling molds )
Learning outcomes#
- Design appropriate objects within the limitations of your process
- Demonstrate workflows used in mold design, construction and casting
Have you answered these questions?#
- Linked to the group assignment page and reflected on your individual page what you have learned
- Reviewed the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials, then made and compared test casts with each of them
- Documented how you designed and created your 3D mold, including machine settings
- Ensured your mold has smooth surface finish, that does not show the production process (by postprocessing if necessary)
- Shown how you safely made your mold and cast the parts
- Described problems and how you fixed them
- Included your design files and ‘hero shot’ of the mold and the final object
Agenda#
Group Assignment#
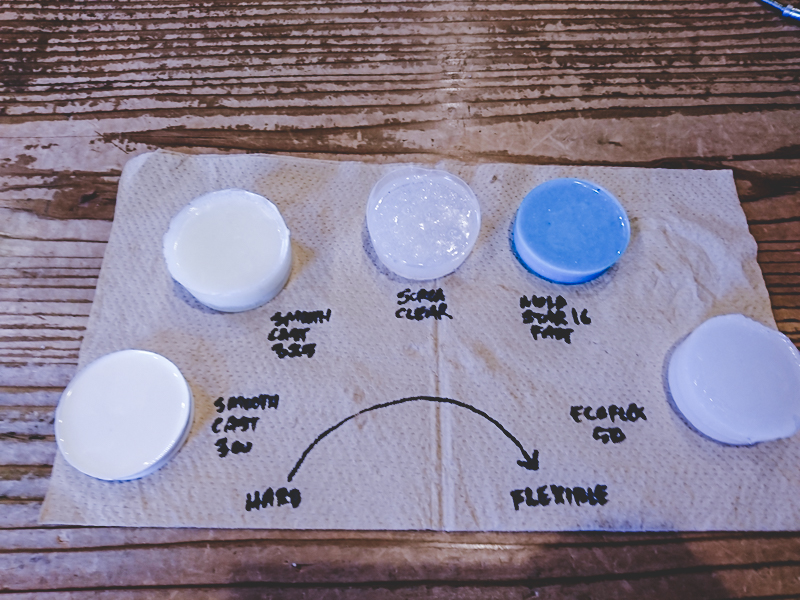

- Labの下記在庫から、各自別々の素材を選ぶ。
- SDSを調べ、主要パラメータなどをリストアップする
- その素材をカップなどを使って少量CASTし、結果を比較する。 (同じ形状、量の方が素材の違いを比較しやすい)
- 計測は Volume でもWeightでもよいが、Weightは1:1 ではないものがあるので注意
- Individual Assignment ではMillingで型をつくるが、Printのプロセスも調べて比較する。プリントをする必要はないが、試したい人は、SkyLabにSLAがある。
- SLA Stereolithography 光造形
SDS#
-
Ferris® File-A-Wax® Carving & Milling Waxes - Freeman Manufacturing and Supply Company
- SDS for blue wax
- Size : 147 x 88 x 37mm (Actual measurement 実測値)
-
Smooth-On Document Library - Technical Bulletins (TB), Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
- MOLD STAR 16 FAST
- SMOOTH-CAST 300
- SMOOTH-CAST 325
- SORTA-CLEAR 37
- TB / SDS / Food Safe Technical Bulletin
- Color: Water Clear Translucent
- Pot Life: 25 minutes
- Cure Time: 4 hours
- Mix Ratio By Volume: 1A:1B
- Mix Ratio By Weight: 1A:1B
- Shore 37A
- Ecoflex 30
Individual assignment#
Design#
- One side moldか、Two side moldかを決めて、デザインをする
- 必ず3D形状をどこかに含むこと。角をフィレットする程度でも構わない。
- ビットの太さ、長さ(彫れる深さに関係)に注意してデザインする
-
モデルは小さくする。切削時間が何時間もかかるので。
-
One side mold type

-
Two side mold type
-
Support Document: Mold Making Tutorial in Fusion360
-
-
Tool Path#
- Software
- MODELA: LABのノートにインストール済
- その他: mods, Fusion360
- Endbit
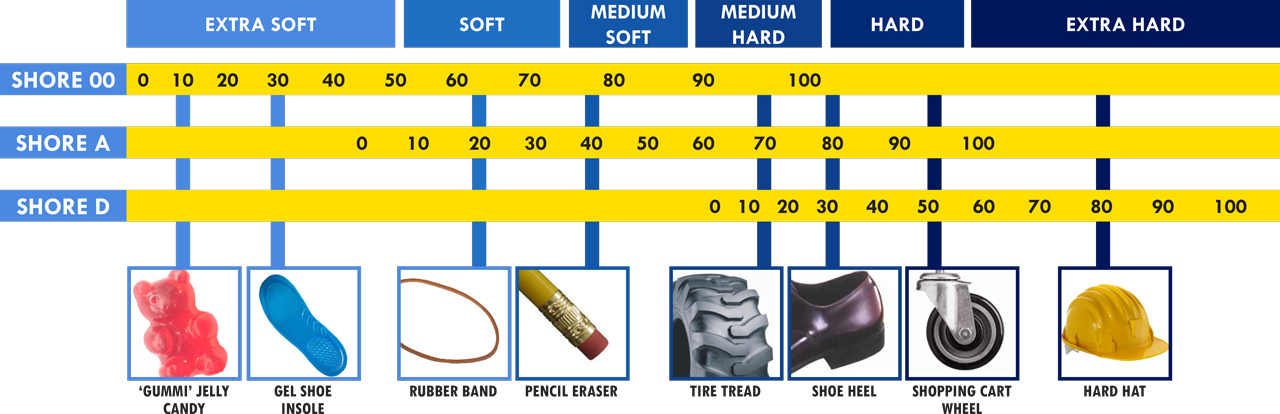
- ⅛inch (3.18 mm) long 4FL SE
- ⅛inch 2FL BN
- 1/16inch 2FL BN
Milling#
-
Machine
- SRM20
-
Tools
- ⅛inch (3.18 mm) long 4FL SE
- ⅛inch 2FL BN
- 1/16inch 2FL BN
Notes on Machining#
Create two types of toolpaths - Rough Cut: a layered path to remove material efficiently - Finish cut: three-dimensional milling like descending a valley and ascending a mountain
- Square end: even a square can be made into the three-dimensional path described above for finishing.
- Ball end: The cutting edge can go into finer areas than square. When cutting horizontal surfaces, it takes more time than square.
- XTRA LONG : Can cut deeper pockets. However, the bite bends, so run-out (shaft shake) is greater. Recommended for this week’s task. Make sure that the shank and collet do not strike the material (especially when trying to dig deeper pockets). For example, taper the walls of the pocket to make room for the shank and collet.
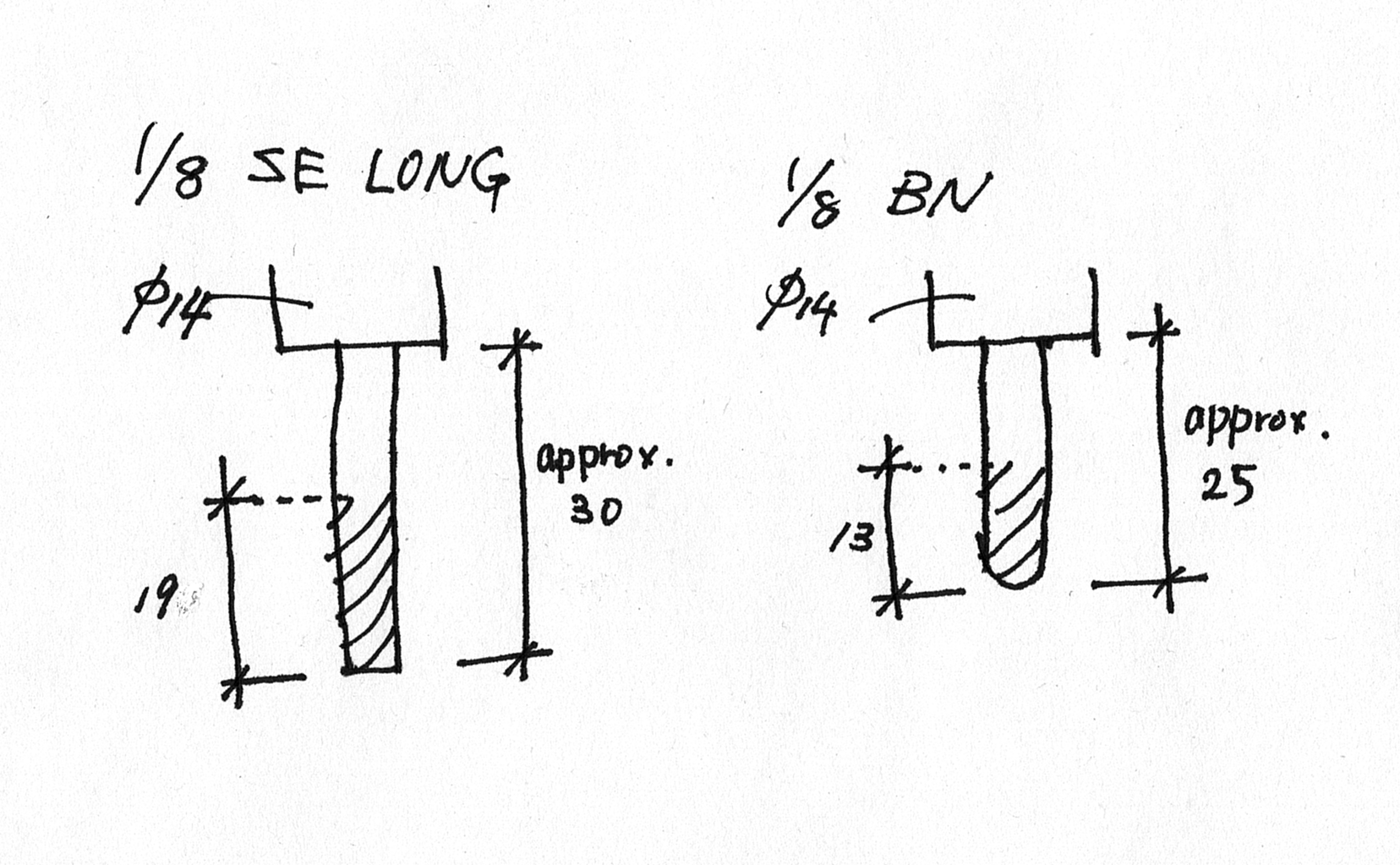
- 型のデザインについて
- Vent(空気の抜け道)の位置
- 気泡を取り除く方法
- stirring(攪拌) : 垂直方向に混ぜるのではなく、水平方向に混ぜると気泡が生じにくい
- pouring(注ぎ) : 水平な天井があるような型なら、少し傾けて注ぐと気泡が入りにくい
- painting(塗る) : 造形の細かい箇所は筆で材料をペイントしてから注ぎ込む
- vacuum(減圧) : デシケーターなどを使い、容器内の気圧を下げて気泡を抜く
- 他、たたく、振動を与えるなど
Polymers#
Polymers consist of repeating molecular units (monomers). Here are examples.
Polyl(lactic acid) (PLA)(ポリ乳酸)#
monomer: lactic acid(乳酸)
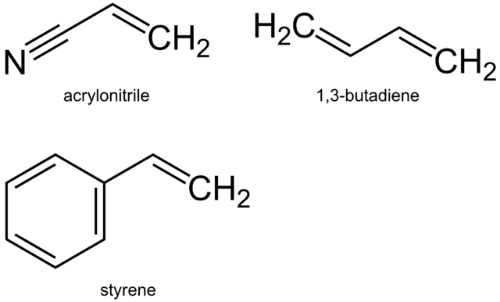
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)#
monomers: acrylonitrile(アクリロニトリル), butadien(ブタジエン), and styren(スチレン)
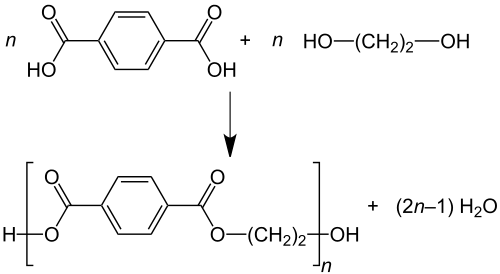
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)#
monomers: ethylene glycol(エチレングリコール) and terephthalic acid(テレフタル酸)
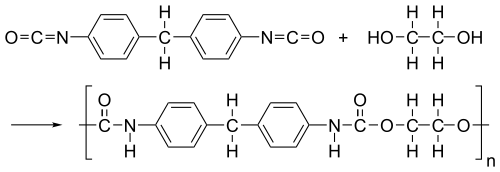
Polyurethane(ポリウレタン)#
monomers: polyisocyanate(ポリイソシアネート), polyol(ポリオール)
SDS of Smooth-Cast 300#
Smooth-Cast 300 consists of Part A and B.
Ingredients of Part A are isocyanates.
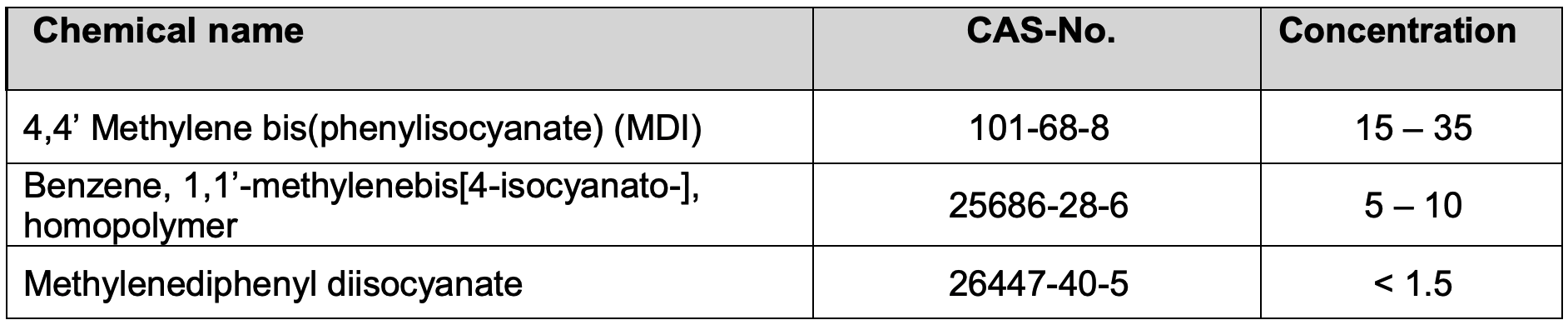
If you want to know what its structure looks like, google it using CAS number like, “CAS:101-68-8“
4,4 Methylene bis(phenylisocyanate)(MDI)
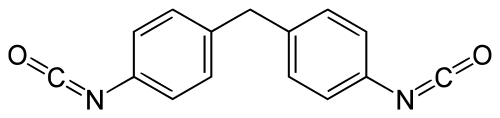
Benzene, 1,1’-methylenebis[4-isosyanato-], homopolymer
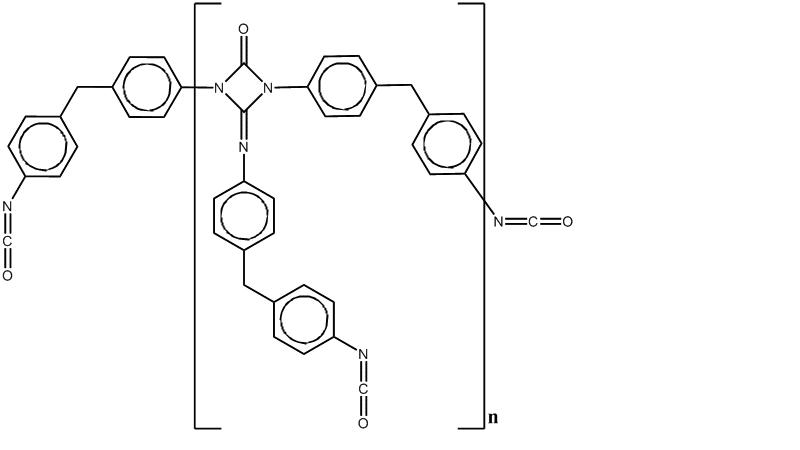
Ingredients of Part B is disclosed in SDS, but it must be polyols, which is containing a bunch of -OH group.




